Jira's integration with CI/CD tools also enables real-time updates on the development work being done. For instance, by linking Jira issues to your CI/CD process, you can see a detailed view of the development work done in the 'Development' section of Jira. You can also view all the commits linked to an issue in the 'Commits' tab, providing transparency and traceability to your development process.
Similarly, in the 'Pull Requests' tab, you can view all the pull requests associated with an issue, promoting code review and collaboration. Lastly, the 'Deployments' tab shows all deployments linked to an issue across all environments, providing a comprehensive view of the deployment history.
Initial JIRA Setup: User Roles, Permissions and Project Creation
To start with, define user roles and permissions in JIRA according to your organization's structure.
Next, create a project to house your CI/CD pipeline. You can select a template or create a custom project as needed. Remember to set up your project's workflow to reflect your release management process.
[Read: How to Create Backups for Jira Cloud]
Next, integrate your CI/CD tools with JIRA. This is typically done through plugins provided by Atlassian or the tool's vendor. The integration will allow JIRA to receive updates from these tools, providing real-time visibility into your pipeline.
Configuring a CI/CD pipeline in JIRA
Once the tools are integrated, you can configure your CI/CD pipeline. This involves creating issues for your pipeline tasks, associating them with the relevant code changes, and updating their status as they move through the pipeline.
Defining Deployment Environments and Release Strategies in JIRA
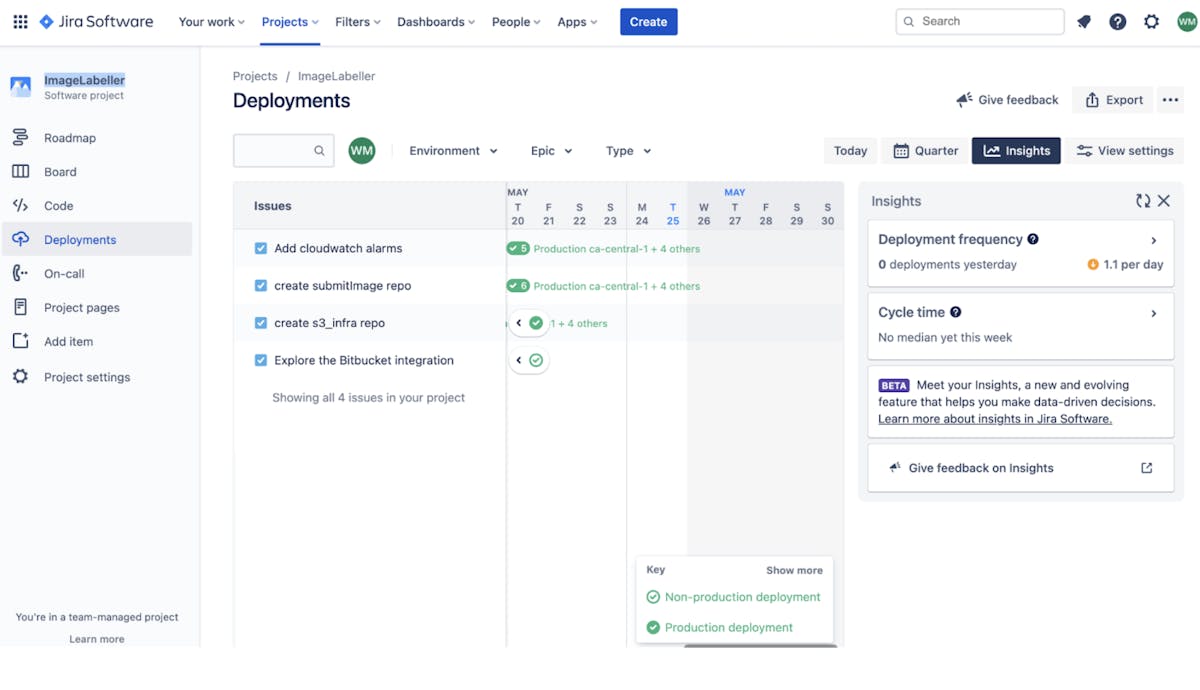
The next step is to define your deployment environments (e.g., staging, production) in JIRA. You can then create versions in JIRA for each release, and associate issues with these versions. This allows you to track the progress of each release and the issues it contains.
Managing CI/CD Deployment using JIRA
With everything set up, it's now time to manage your CI/CD pipeline using JIRA. This is done primarily through JIRA's workflows and boards. Workflows allow you to visualize your pipeline's process, while boards provide a bird’s-eye view of your pipeline's current status.
JIRA boards can be customized to display the data most relevant to you, providing a dynamic view of the state of your CI/CD pipeline. You can view issues by status, assignee, release version, and more.
JIRA's versioning feature is key to managing releases. You can track which issues are part of a release, the status of the release, and when the release was or will be deployed.
Advanced JIRA Techniques for Optimal CI/CD Deployment
Using Custom Fields and Filters for Effective Tracking
JIRA's custom fields and filters allow for precise tracking of issues in your CI/CD pipeline. Custom fields can capture specific data about your issues, while filters can help you find and organize issues based on these fields.
Implementing Automated Triggers and Post-Functions
Automation in JIRA can save time and reduce errors in your CI/CD pipeline. Triggers can automatically transition issues when certain events occur in your CI/CD tools, while post-functions can perform actions after an issue transitions, such as updating fields or sending notifications.
Utilizing JIRA Query Language (JQL) for Advanced Search
JQL is a flexible and powerful tool for finding issues in JIRA. With JQL, you can create complex queries that find issues based on any combination of fields. This is extremely useful for reporting and for creating custom views of your pipeline.
Key Challenges in CI/CD Deployment via JIRA and Solutions
Handling Complex Workflows and Large Releases
As your CI/CD pipeline grows in complexity, managing it in JIRA can become a challenge. However, by using JIRA's advanced features like custom workflows, filters, and automation, you can keep things manageable.
Ensuring Continuous Monitoring and Rapid Incident Response
With constant changes in the pipeline, it's crucial to monitor the system continuously and respond to incidents quickly. JIRA’s integration with monitoring tools and its robust notification system help in achieving this.
JIRA's wide range of plugins and APIs help overcome interoperability issues, ensuring seamless communication between different tools.
Measuring Success: JIRA Metrics and Reporting for CI/CD Deployment
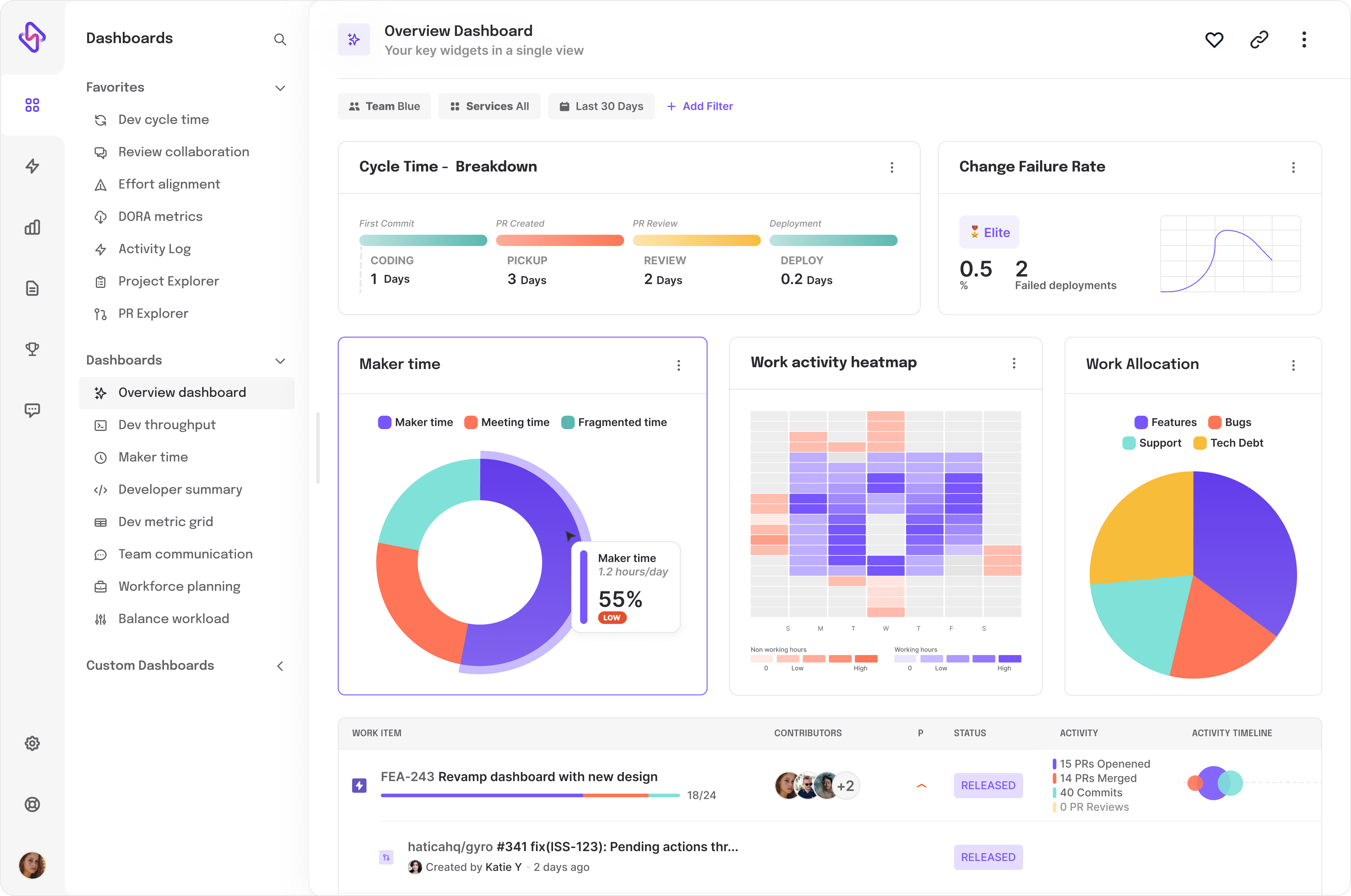
JIRA provides numerous KPIs for tracking the health of your CI/CD pipeline. These include lead time, deployment frequency, change failure rate, and mean time to recovery.
Using JIRA’s Reporting and Dashboard Features
JIRA's powerful reporting and dashboard features provide a visual representation of your pipeline's KPIs, making it easy to interpret and act upon them. For a deeper understanding of how to utilize Jira to its full potential, consider exploring Hatica's comprehensive guide on Jira Templates.
Interpreting CI/CD Metrics for Continuous Improvement
By closely monitoring and interpreting your CI/CD metrics, you can identify areas for improvement and take steps to optimize your pipeline.
Sustaining CI/CD Excellence with JIRA
JIRA's continuous evolution, combined with its adaptable and potent platform, ensures its position as a top-tier tool for managing CI/CD deployments. This constant innovation means you'll always have access to the most up-to-date project management tools and strategies. Dive deeper into the world of efficient project management with Hatica's comprehensive guide on Jenkins-Jira Integration.
Part of leveraging the power of JIRA involves keeping abreast of its latest features and how they can be used to optimize your CI/CD pipeline. For example, using JIRA's extensive templates can significantly improve your issue-tracking and resolution process. Hatica's enlightening article on JIRA templates further illustrates how you can customize these templates to suit your project's specific needs.
By strategically leveraging JIRA, your CI/CD pipeline can become an exceptionally well-functioning apparatus, promoting efficiency, quality, and rapidity in your software delivery process.