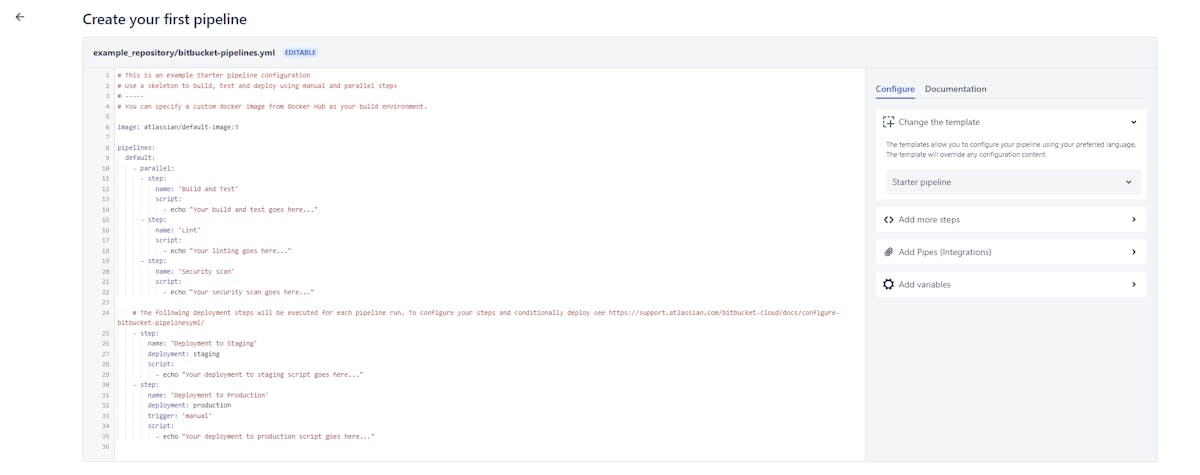
In this example pipeline, caching is enabled by adding the "caches" section to the step. The "node" cache is used to cache the dependencies installed by npm. When the pipeline is run again, the dependencies are loaded from the cache, which saves time.
2. Use Parallelism to Speedup Testing
Parallelism is a feature of Bitbucket Pipelines that allows developers to speed up testing and improve the overall efficiency of their CI/CD process. Parallelism refers to the ability to divide a single job into multiple smaller jobs that can run concurrently on different machines, reducing overall execution time.
Bitbucket Pipelines runs each job sequentially, one after the other, by default. However, by using parallelism, you can run multiple jobs in parallel, significantly speeding up your testing process.
To use parallelism in Bitbucket Pipelines, your pipeline steps must be defined in a way that allows for parallel execution. For example, in your pipeline configuration file, you can define multiple test scripts and then run them in parallel using the parallel keyword.
The parallel steps you configure will start at the same time in our auto-scaling build cluster and will finish before the next serial step runs. It is primarily intended for large suites of automated tests, but it can also be used for large parallelizable computing tasks.
Running steps in parallel provide faster feedback. This saves developers valuable time that would otherwise be spent waiting for the build.
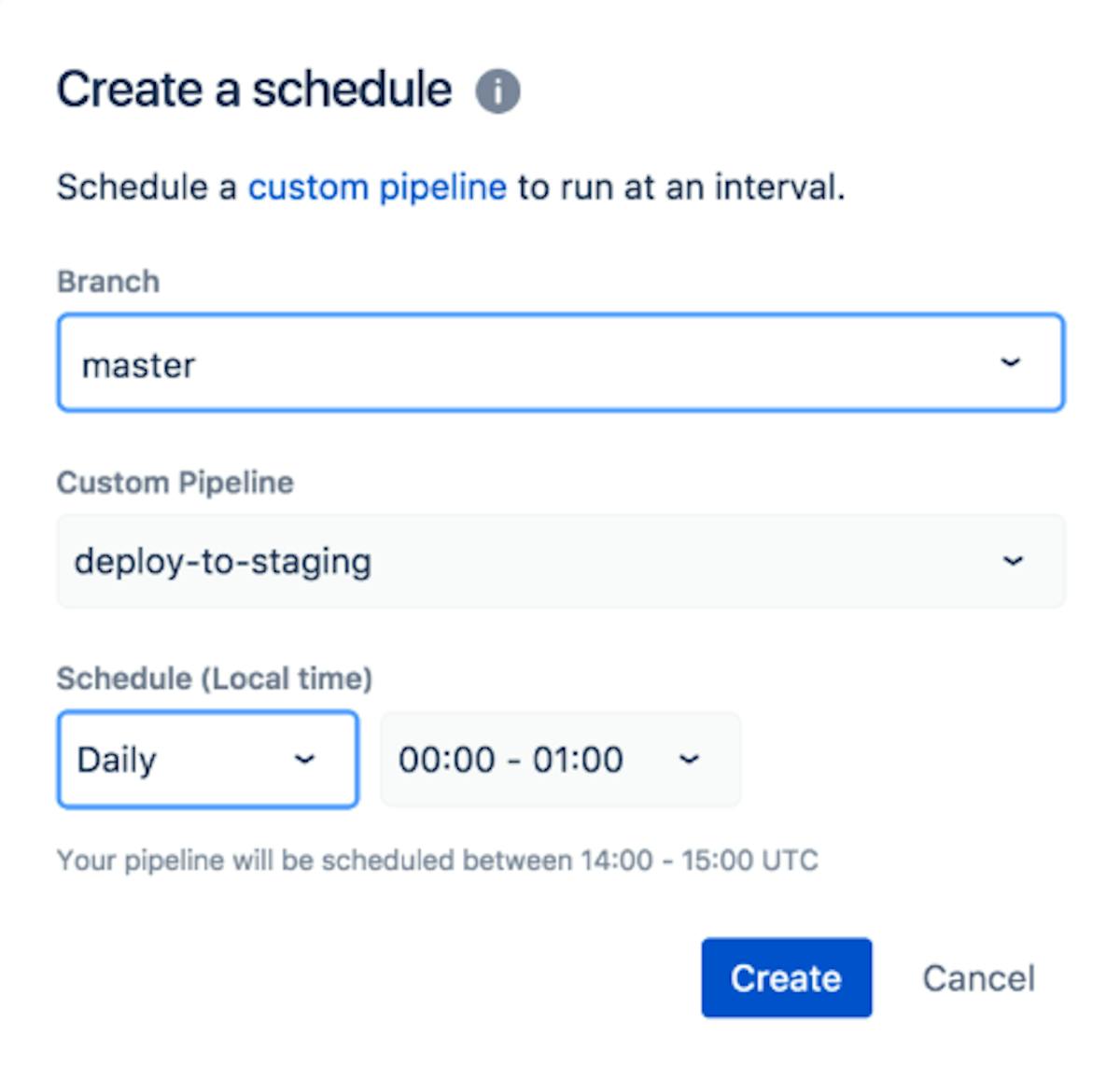
3. Scheduled pipelines
Bitbucket Pipelines is an excellent solution for developers who require immediate feedback when changes are committed. It's a simple continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) solution for automating the build, test, and deployment processes.
However, there are many situations in which builds must be run on a regular basis, even if the code base has not changed. For example, longer-running nightly builds, daily or weekly deployments to a test environment, data validation and backups, load tests, and tracking performance over time. Furthermore, there are jobs and tasks that are unrelated to code changes but must be completed on a regular basis.